AEROSE Campaigns
AEROSE
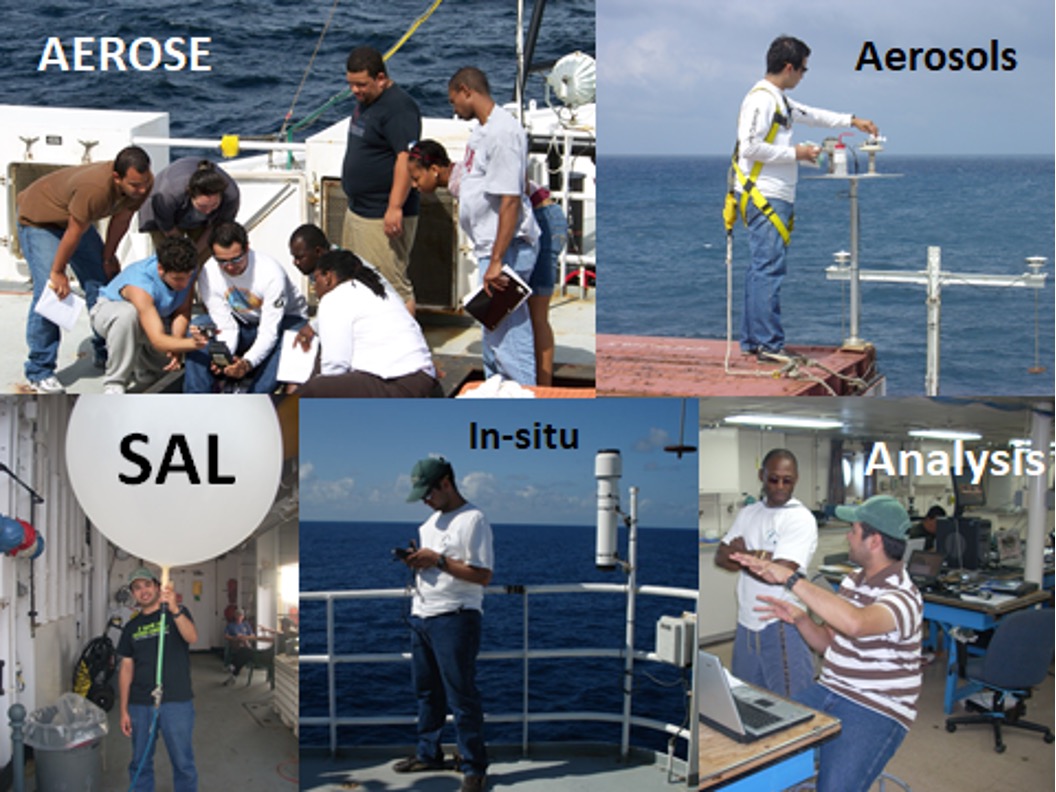
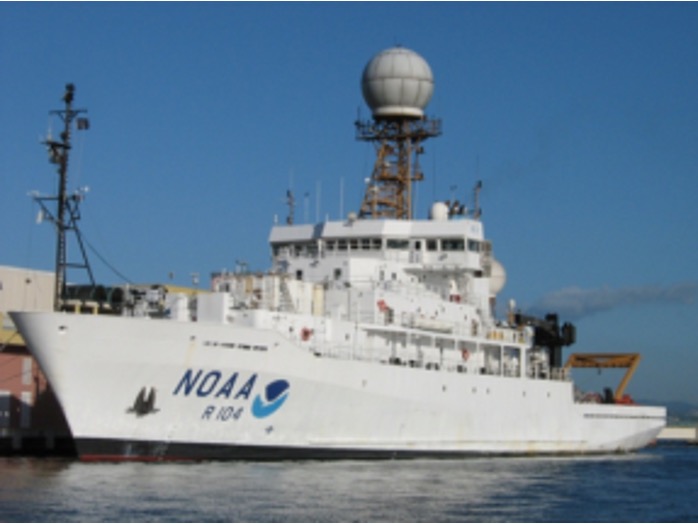
The trans-Atlantic Aerosol and Ocean Science Expeditions (AEROSE) are a series of campaigns conducted on the Ronald H. Brown NOAA ship. AEROSE mission focuses on measurements that characterize the impacts and evolution of aerosols from Africa as they transit the Atlantic Ocean. Measurements will serve the science community with key dataset of aerosol properties and facilitate improvement in satellite retrievals and climate models.


AEROSE Campaigns
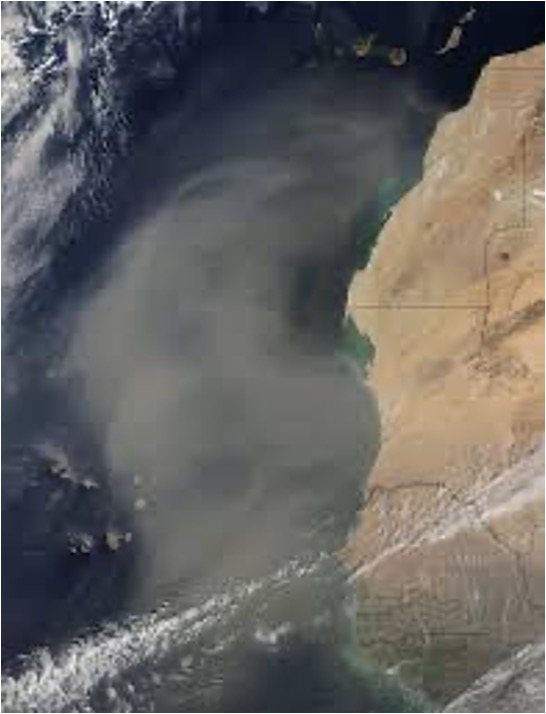
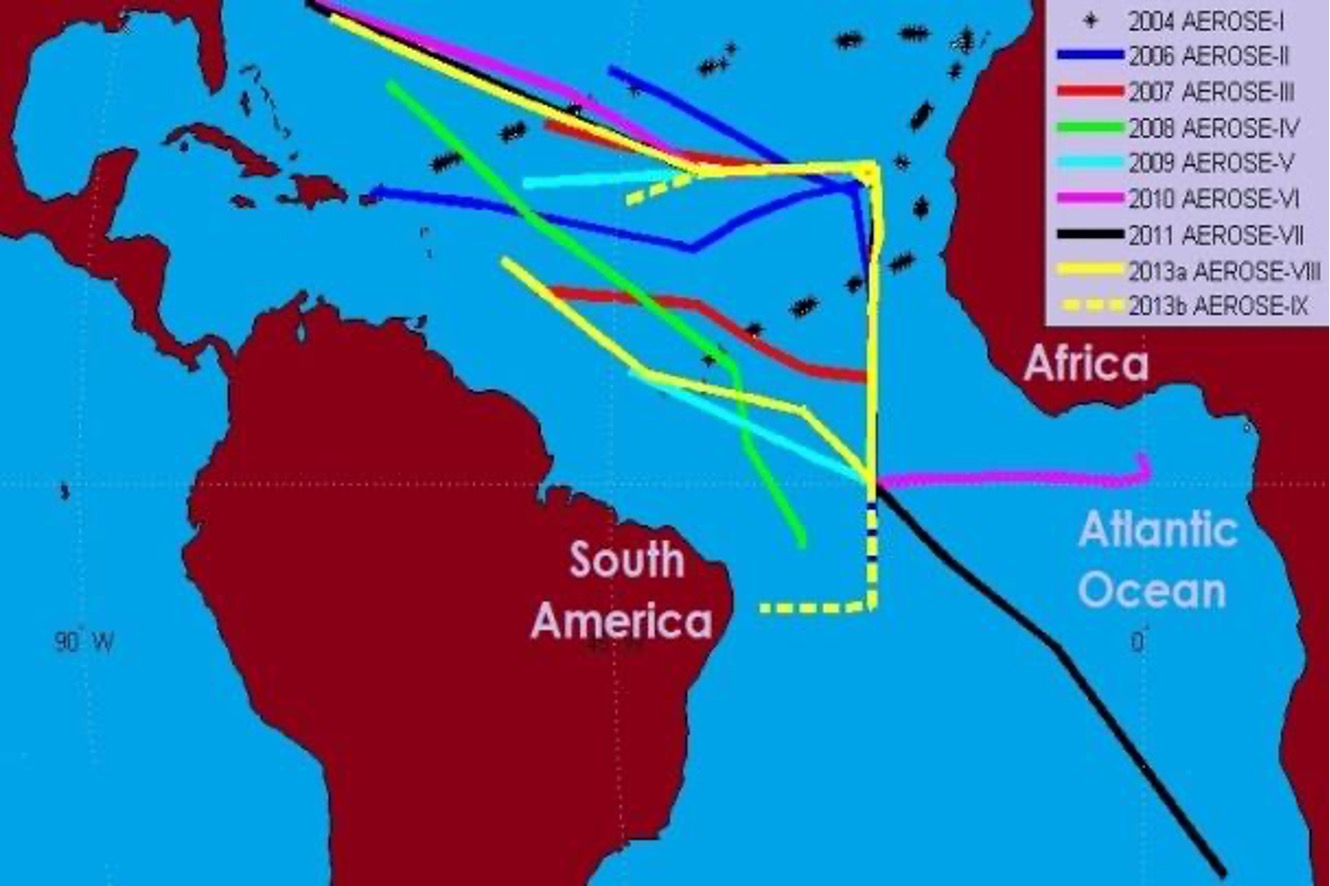
A total of 12 AEROSE campaigns have been conducted from 2004 to 2019 covering most of the Atlantic Ocean, especially the tropics to the west African coast. This specific area is where most of the measurements are done in order to understand the physical and chemical properties of the Saharan Air Layer (SAL). Not only we can find dust particles in this region, but also smoke from biomass burnings from central Africa. Major dust and smoke events were measured during some campaigns.


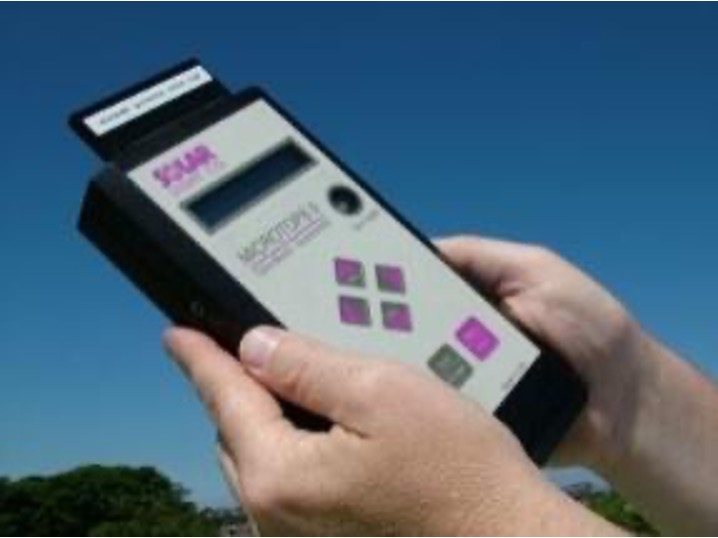
Microtops II Sunphotometer
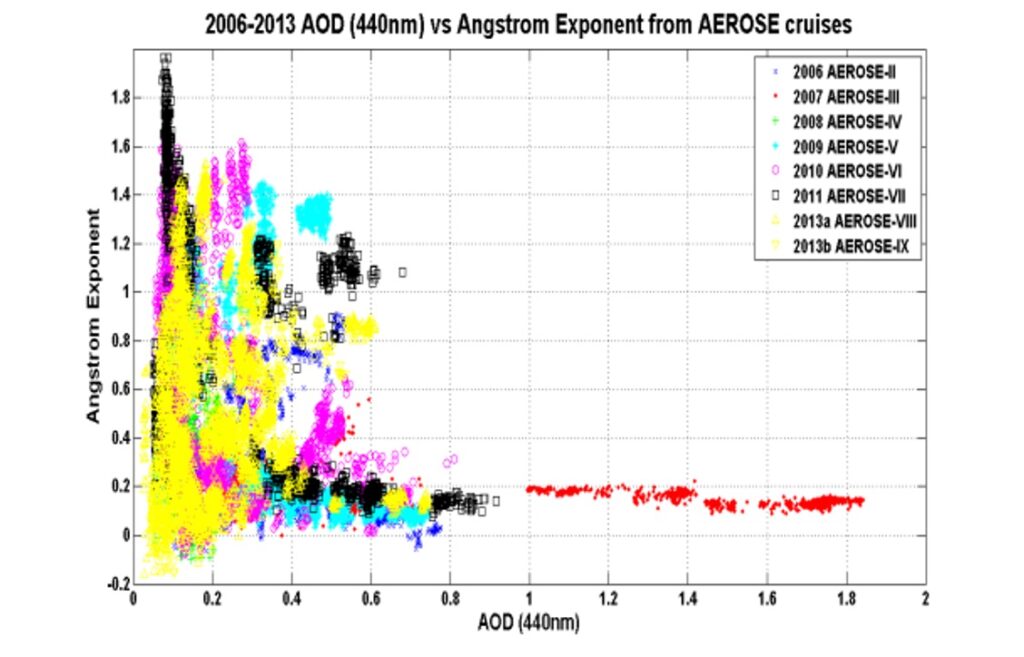
One of the instruments onboard the ship for aerosol measurements is the hand-held Microtops II sunphotometer. This multi-channel device can get the Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and derive the Angstrom Exponent in order to distinguish what particles are aloft. The 2007 AEROSE-III cruise captured a major dust event.

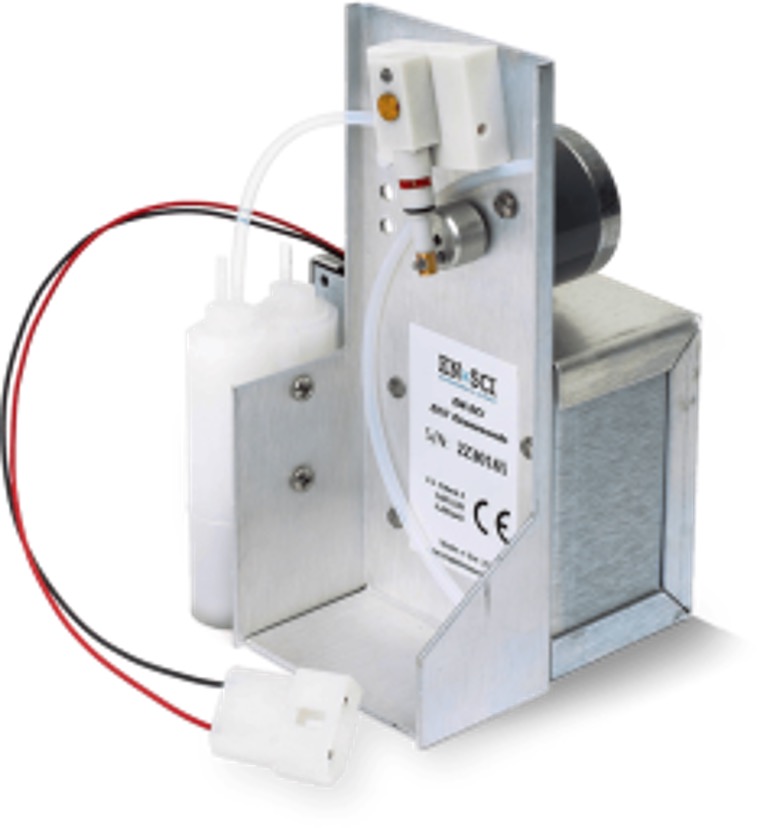
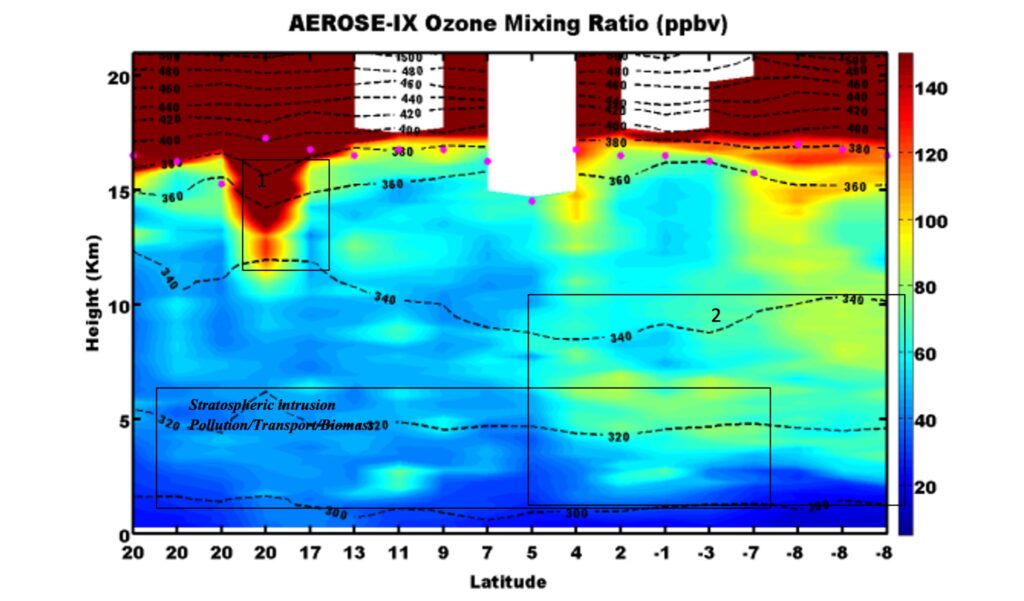
Another feature of the AEROSE campaigns are the radiosonde and ozonesonde launches. There could be a total of 100 radiosonde launches per cruise (roughly 4 launches every day). And up to 20 ozonesondes are launched each campaign in order to detect stratospheric intrusion and transport of pollution/biomass. Most of these launches were coordinated with satellite overpasses for calibration/validation purposes. These profiles of the atmosphere are also a unique data collection of dust transport over the Atlantic.